In the age of ubiquitous internet connectivity, securing your Wi-Fi network is paramount. With the proliferation of smart devices and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, knowing who is connected to your Wi-Fi network is essential for safeguarding your privacy and network integrity. In this guide, we’ll explore various methods to check who’s connected to your Wi-Fi network and how to ensure its security.
1. Accessing Your Router’s Admin Panel:
- The primary method to check who’s connected to your Wi-Fi network is by accessing your router’s admin panel. You can usually do this by typing your router’s IP address into a web browser. Common IP addresses for routers include 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1.
- Log in using your router’s username and password. If you haven’t changed these from the default settings, you can typically find them on the router itself or in the documentation.
- Once logged in, look for a section labeled “Connected Devices,” “DHCP Client List,” or similar. This section should display a list of devices currently connected to your network, along with their IP addresses, MAC addresses, and sometimes device names.
2. Using Network Monitoring Apps:
- Several third-party apps and software tools are available for monitoring your network and identifying connected devices. These tools often provide more detailed information than your router’s admin panel, such as device type, manufacturer, and connection history.
- Examples of network monitoring apps include Fing, NetSpot, and Wireless Network Watcher. These tools are typically available for both desktop and mobile platforms and offer user-friendly interfaces for monitoring and managing your network.
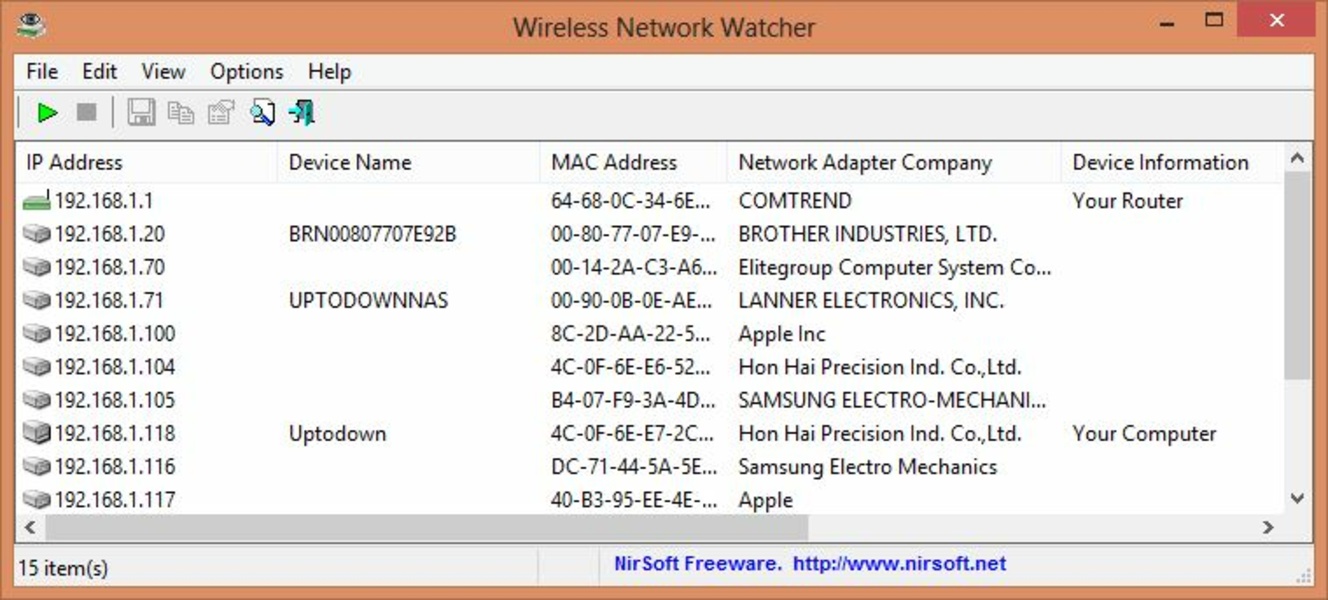
3. Utilizing Built-in Operating System Tools:
- Most modern operating systems offer built-in tools for viewing connected devices on your network.
- On Windows, you can use the Command Prompt and enter the command “arp -a” to view a list of devices connected to your network along with their IP and MAC addresses.
- On macOS, you can use the Network Utility tool or the Terminal and enter the command “arp -a” similarly to Windows.
- On mobile devices, you can often find information about connected Wi-Fi networks and devices in the settings menu.
4. Setting Up MAC Address Filtering:
- Another method to control who can connect to your Wi-Fi network is by enabling MAC address filtering on your router.
- Every device connected to a network has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. By configuring your router to only allow connections from specific MAC addresses, you can effectively control access to your network.
- Keep in mind that MAC address filtering is not foolproof, as MAC addresses can be spoofed. However, it adds an extra layer of security to your network.

5. Securing Your Wi-Fi Network:
- In addition to monitoring connected devices, it’s essential to secure your Wi-Fi network to prevent unauthorized access.
- Use a strong, unique password for your Wi-Fi network. Avoid using default passwords or easily guessable phrases.
- Enable WPA2 or WPA3 encryption on your router to protect data transmitted over your network.
- Regularly update your router’s firmware to patch security vulnerabilities and ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion:
Regularly checking who’s connected to your Wi-Fi network is a crucial aspect of maintaining network security and privacy. By following the methods outlined in this guide and implementing appropriate security measures, you can effectively manage and protect your Wi-Fi network from unauthorized access and potential threats. Remember to stay vigilant and proactive in safeguarding your network against evolving cyber risks.





